Antimicrobial action adjustments
PROTECTIVE TEXTILES USE CASE
Used in hospitals and cleanroom production facilities of pharmaceutical components, biologicals and vaccines, they can be in continuous contact with dangerous viruses, bacteria and fungi and require a quick response and high dosage of antimicrobial additive to guarantee safe working conditions. In RELIANCE, Cu-SMIN will smartly respond to human body temperature to release the antimicrobial agent during use. Moreover, leaching will be avoided during non working time and washing, to allow their long-term efficiency.
HOME APPLIANCES USE CASE
In our daily environments, the highest number of microorganisms are found in our kitchens. A study reveals that on average, the salad drawers alone in a frost-free home fridge contained 7,850 bacteria units per square centimeter. At the same time, a safe number of bacteria units per square centimeter for innocuous food preparation is between 0 and 10. Considering the risk of microbes being in contact with food, an extra dosage of antimicrobial additives will be pursued for this use case application, with the pH of human hand sweat as a switch on mechanism of selected valves.
АUTOMOTIVE INTERIOR COMPONENTS USE CASE
The long-lasting action required for this application limits the possibility of antimicrobial leaching and therefore the high number of microbes which could be found in this environment are addressed by an extra dosage of AMPs on the Cu-SMIN surfaces, to act synergistically to the Cu presence.



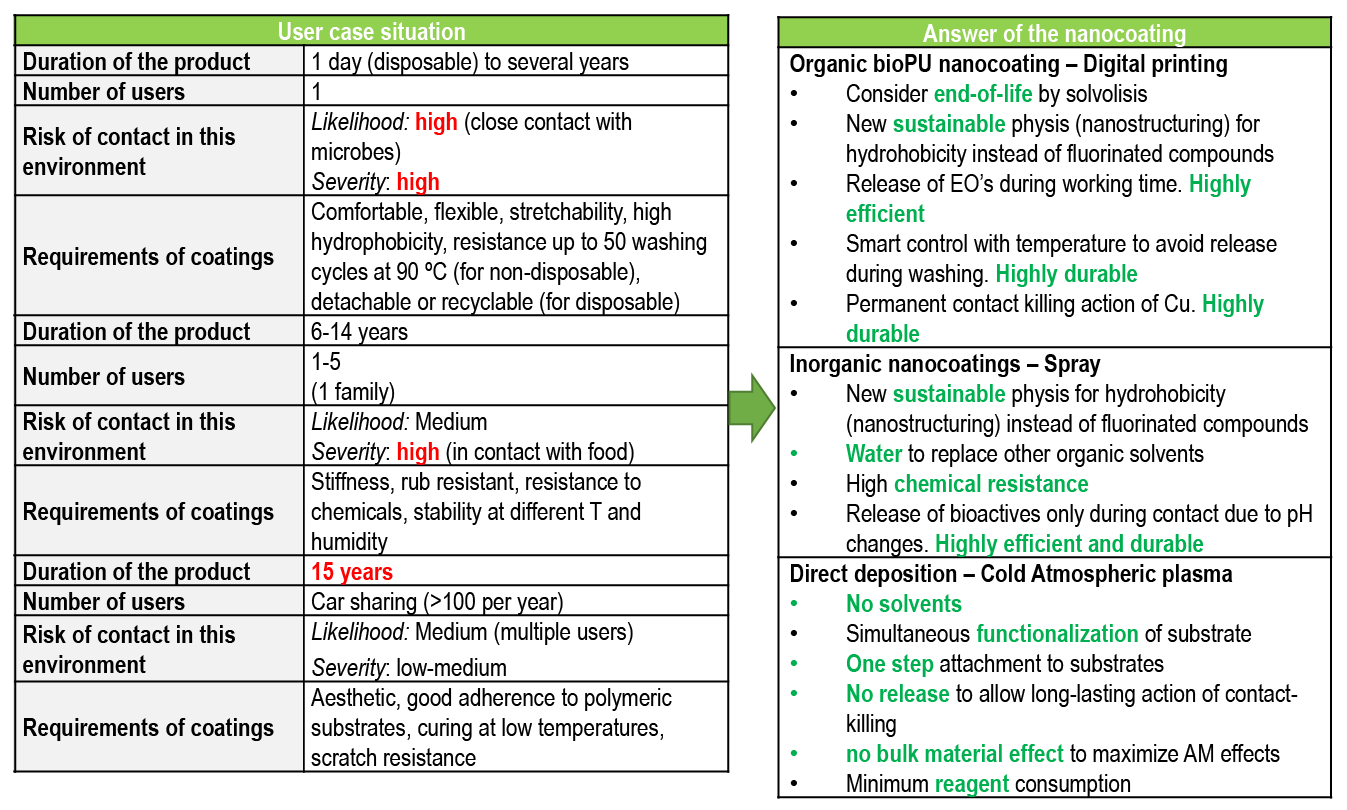
Table 2. Requirements for the specific use cases of nanocoatings in terms of durability of the antimicrobial action
Antibacterial efficacy validation
Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are selected as their cell-wall structure may react differently to antimicrobials. The selected specific pathogenic bacteria are notorious for lethal cases. It had been demonstrated that their transmission often occurs through surfaces or objects contaminated by saliva or nasal secretions.
- Staphylococcus aureus - an asymptomatic colonizer of human nares, with approximately 30% of individuals permanently colonized. Also, a leading cause of endocarditis, bacteraemia, osteomyelitis and skin and soft tissue infections.
Did you know that S. aureus isolates represent 29 % of all reported bacterial isolates in Europe. Moreover, S. aureus rapidly acquires resistance to antibiotics with a growing number of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) cases difficult to treat.
- Neisseria meningitidis - a member of the normal nasopharyngeal microbiome in healthy individuals which can cause septicemia and meningitis in susceptible individuals.
- Influenza A virus (pH1N1) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) will be studied for antiviral properties. Within a short timeframe, humanity has experienced two pandemics caused by these viruses. They are also of particular importance because of their high social impact, their ease of transmission and ability to contaminate surfaces.
Antifungal tests will be made with a wide range of fungi (Aspergillus niger, Penicillium funiculosum, Paecilomycesvariotii, Gliocladium virens and Chaetomium globosum), known to be abundant in-home appliances causing food spoilage.

Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Health and Digital Executive Agency (HADEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
© All Rights Reserved 2025 | Reliance-HE
Designed and Developed by Europroject

