
August 25, 2025
Making the best use of friendly chemistry with the sustainable atmospheric plasma coating process

Minimal consumption of chemistry and energy with maximum effectiveness is possible.
To have maximum and lasting effect, the sustainable antimicrobial active ingredients developed in the RELIANCE project should be pure and stay on the surfaces of products. Even better if this can be achieved without the help of additives and solvents, and ideally, consuming as little energy as possible. Without forgetting that it shouldn’t cost too much.
All these benefits are now possible with atmospheric plasma deposition, named by RELIANCE partner MPG “molecular plasma coating”. Simply put, it works by replacing aggressive chemical energy with a little bit of electricity. An electrical field excites an inert gas like nitrogen, creating a “plasma” (like in the neon lamps). This “cold” plasma is then used to apply coatings and permanently bond organic molecules onto any substrate.
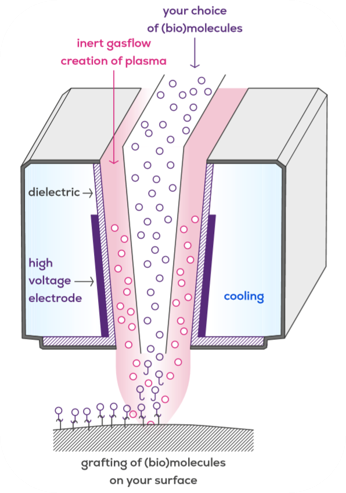
The plasma excites the surface and the chemistry, they react, and here we go with having a coated, functional surface. This can be done on an industrial scale.
Contrary to other plasma processes, this one takes place at atmospheric pressure, room temperature and at extremely low energy levels. Unlike the previous vacuum-based batch processes, the cold atmospheric plasma process is continuous. It is both environmentally sustainable and enables working with highly sensitive molecules such as the peptides being developed in the RELIANCE project. The bonus for healthcare applications is the possibility to use pure active ingredients, without the need for solvents, binders or curing agents that often become a biocompatibility hurdle. The low energy and temperature plasma allows for a wider range of organic chemistry and biomolecules, which is the main reason it was chosen as one of the coating methods in the RELIANCE project.
Tangible reduction in environmental impact
MPG’s process numbers speak for themselves when evaluating impact on the environment. The consumption of chemical precursors is in the order of less than 1 milligram per square meter of treated area, compared to grams for traditional coatings. The use of energy is in the order of 0,002 kWh per square meter when treating films continuously, almost negligible compared to the energy needed to cure and dry traditional wet coatings.
A European technology with EU support from member states Molecular Plasma Group was created as a spin-off from the Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST) and the Flemish Institute for Technology Development (VITO). Its revolutionary cold atmospheric plasma technology has been described as ‘magic’ due to its limitless application potential. It is already being used in healthcare, aerospace, automotive, electronics and other applications. The machines are made in Belgium from mostly EU-sourced components.
For more information about this revolutionary technology, contact Molecular Plasma Group, Luxembourg





Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Health and Digital Executive Agency (HADEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
© All Rights Reserved 2025 | Reliance-HE
Designed and Developed by Europroject

