Home appliances are commonly used in our daily life, with their surfaces being exposed various sources of virus and microbes, and human bodies. The research work in RELIANCE project addresses the above by bringing to the European consumers a set of innovative anti-microbial and antiviral coatings for everyday life products and applications.
While there are high expectations for some surfaces, such as the glass shelves of refrigerators, to be capable of suppressing bacteria or virus proliferation, the same applies to the technologies behind these surfaces’ functionalities. The novel biobased and self-disinfectant compounds RELIANCE develops will be added to the new nanocoatings, triggering a contact-killing action against bacteria and viruses. However, the matrix of the coating in which these newly designed active ingredients will be embedded represents an exciting challenge in itself. Through chemical design and surface nano- structuration, RELIANCE aims at intrinsically offering virus and microbe-repelling coatings, with a global antimicrobial action.
In the recent years, a large amount of omniphobic and repellent coatings, both inorganic and organic, were developed that were based on fluorine compounds. At the same time, European citizens are becoming increasingly concerned with health and environmental issues due to persistent chemicals waste and regulations expected to impose further restrictions on the use of controversial chemicals, and even mandate their overall replacement. Some fluorine-based chemicals are on the list.
All of the above calls for a new, technically ambitious approach, reflected in RELIANCE work package three, led by partner POLYRISE SAS. Their team focuses on the design and development of hybrid nanocoatings. The work activities so far have led to the obtaining of the first sol-gel-based hybrid inorganic-organic coatings exhibiting both pronounced hydrophobic features and dynamic oleophobicity. In other words, oily liquid or aqueous-based dirt-stain solutions will roll off on such coated surfaces without wetting and soiling them, meaning that the new hybrid coatings will achieve these characteristics without using fluorine-based compounds.
To impart a kind of omniphobicity, hybrid coatings based on functionalized nanosilica and low surface energy sol-gel and siloxane networks were developed, to prepare the coatings of desired transparency for application on substrates such as glass or stainless steel, commonly used in home appliances. The transparency and good aesthetics are assessed by Haze Measurement for clarity of the coated substrate, the mechanical resistance is assessed by hardness, while hydro- and oleophobicity are assessed by both Water or Hexadecane Contact Angle. Along with liquid repellency, these are the specifications for such coatings and formulations, enabling the achievement of the following characteristics when applied on glass substrates:
| Property | Characteristics | Values |
| Transparency | Transparency | 0,3 % |
| Mechanical resistance | Hardness ISO | |
| Easy-to-clean | Water Contact Angle | 98° |
| Hexadecane Contact Angle | 38° |
Oleophobicity can also be demonstrated through the behaviour of an olive oil droplet on the coated surface that effortlessly rolls off glass, without wetting it.
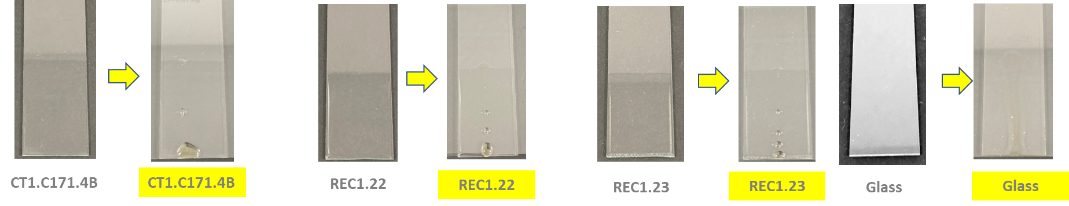
The picture below shows glass-coated substrates obtained by a dip-coating process followed by a thermal curing process at a moderate temperature of 160°C.
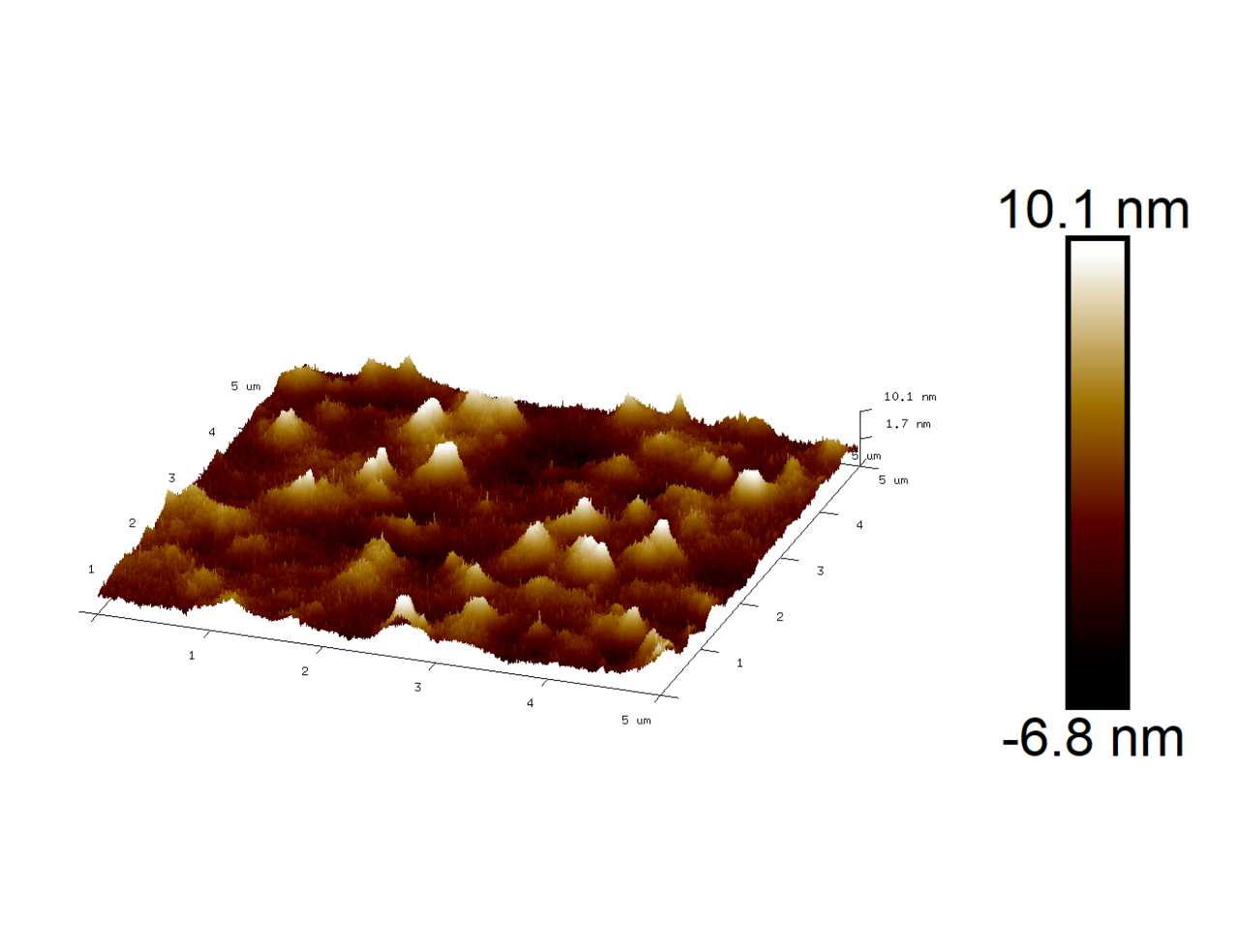
As an objective of the project, the nano structuration of the coated surface could also be observed and determined with Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), displayed in the image below:
To conclude, the development of the coatings must also achieve sustainable development targets. In addition to no fluorine compound use, the new hybrid coatings will be mostly based on aqueous composition while addressing the need for being compatible with spray application deposition. These are the next challenges we are going to tackle in RELIANCE.
Stay tuned!