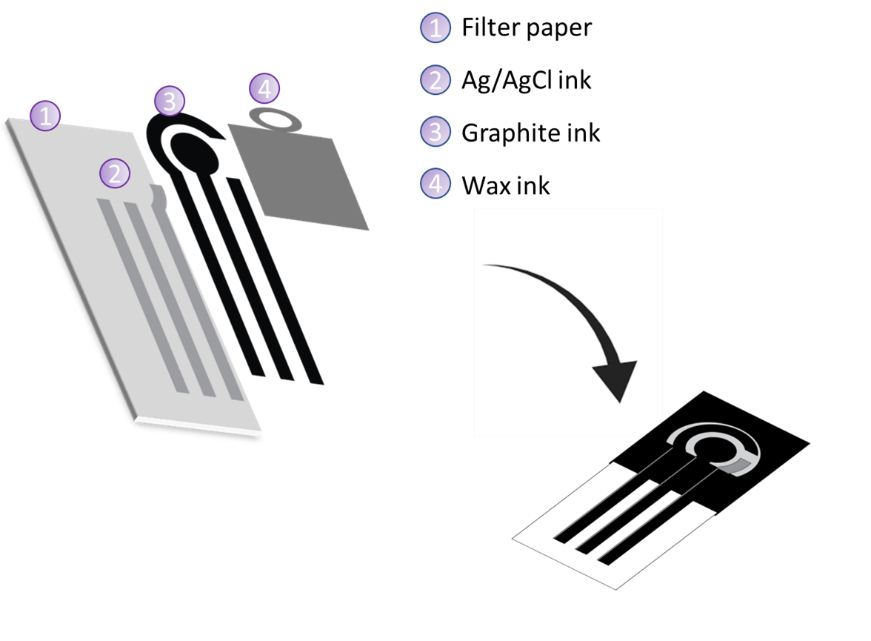
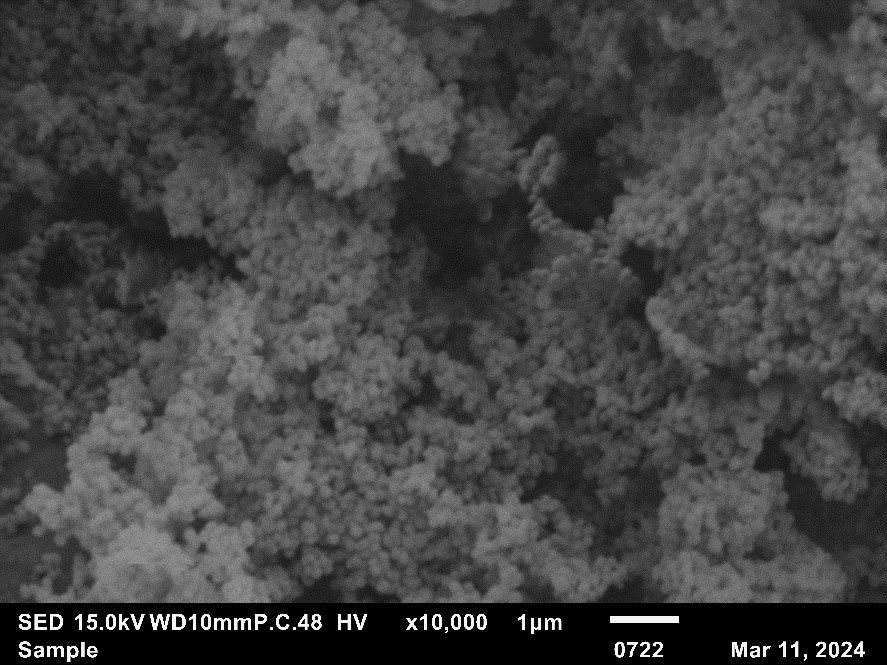
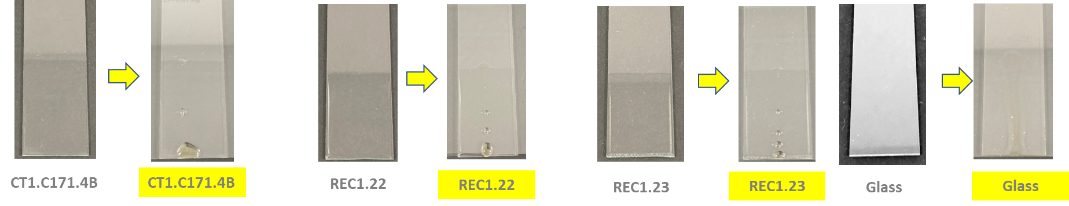
The spring blossoms in May, flourishing in possibilities for RELIANCE synergy activities as well. As an important tool to broaden the impact of collaborative EU projects, they remain key enablers for knowledge exchange and capacity-building, fostering opportunities for enlarging their reach.
RELIANCE and sister project MIRIA recently held a dedicated meeting to discuss more closely potential cooperation. MIRIA focuses on developing a wide range of antimicrobial nanocoatings for use in hospitals and other settings where cross-contamination and contagion risks are significantly high. The coatings they develop will be validated in a semi-real environment of an operating theater, very closely resembling the ones in hospitals. In addition to the differences in the coating deposition techniques applied in the projects, MIRIA’s coatings are primarily based on the use of nanopowders, with graphene being in the limelight. Besides having Millidyne as a common partner, another point of convergence relies on the employment of sol-gel coating formulations on various substrates, such as textiles, polymers, glass, and metals, while using same antiviral material like the Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2.
Some actions deliberated upon by the projects’ teams were joint presentations in workshops and webinars, working together in the area of socio-economic impact analysis of the innovative coatings, testing and validation of these new technologies, comparing the antiviral and antimicrobial aspects and the efficiency of the different coatings.
Just few days earlier, RELIANCE and NANOBLOC coordination and Communication-Dissemination teams conducted a productive introductory discussion to explore the potential cooperation. Both projects focus on designing and developing high-performance, sustainable nanocoatings with enhanced antimicrobial, antiviral, and antifungal properties for various industrial applications. The teams discussed the differences in their coating deposition technologies too.
They identified high potential for collaborating, such as producing dissemination materials that highlight the variations in antimicrobial nanocoatings techniques and their impact on aging, durability, ecotoxicity, and microbial response efficiency. Another collaborative activity could involve publishing of co-authored recommendations for new standards in antimicrobial coatings characterization, tailored to specific applications.
By combining efforts, RELIANCE, MIRIA, and NANOBLOC can jointly explore diverse possibilities, enhancing the projects’ impact and working together to promote safer and healthier surfaces through innovative nanocoating technologies in the EU.
Stay tuned for more updates on our collaborative journey!